How Can Researchers Increase The Confidence Business Decision Makers Have In Qualitative Data
-
9 Tips to Conducting Accurate Qualitative Research
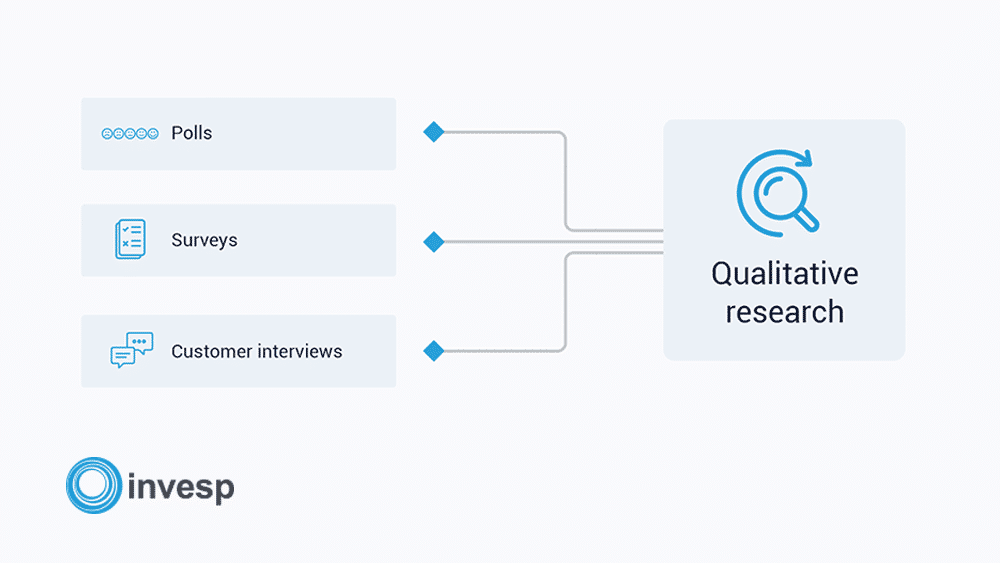

Customers don't recall like nosotros do. And similarly, what we may think looks or sounds right for our company and website, or what may be a main motivator of visitors, could (and is most likely) completely off.
Elizabeth Wellington explains;
"Customers give information that reveals their attitudes (how they call up they should acquit) rather than behaviors (how they actually make decisions)"
But conversions and the path that leads to those conversions is highly driven by the client. The image of a funnel is what comes to mind when many think of conversions, however, because the customer is irrational and highly distracted, it looks more than like this:
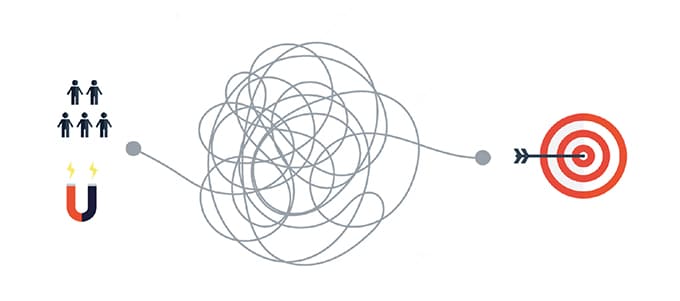
There are ways of conducting qualitative research to assemble customer data and understand more than most what they are thinking, what is motivating them.
When is a qualitative approach needed:
- Piffling is known or present understanding is inadequate
- Making sense of complex situations or social processes
- Acquire from participants about their experiences (behavior, motivations, opinions)
- Construct a hypothesis/theory from information
- Empathize phenomena deeply and in detail
You're essentially putting an organized framework on the messiness of life:
"Chaos oftenbreeds life, whenorder breeds habit."Henry Adams
But one must be wearied with some of the results considering surveys and polls aren't always accurate. Results of those qualitative studies aren't always authentic. There is a scientific discipline in the way that you ask and how you ask it (the method to use).
Susan Farrell explains;
"Write neutral questions that don't imply particular answers or give abroad your expectations." Keep it brusque. Every extra question reduces your response rate, decreases validity, and makes all your results doubtable."
Qualitative research participants ofttimes reply something, but there subconscious and actions do something entirely different. Many studies take been conducted on how faulty relying on qualitative information can be. Participants tend to say the kickoff thing that comes to listen or what they think they want. But yous dig deeper to realize that at that place's a lot more than than you must be uncovered, and what they call up they desire or why they remember they choose is a product or service isn't the true motivation.
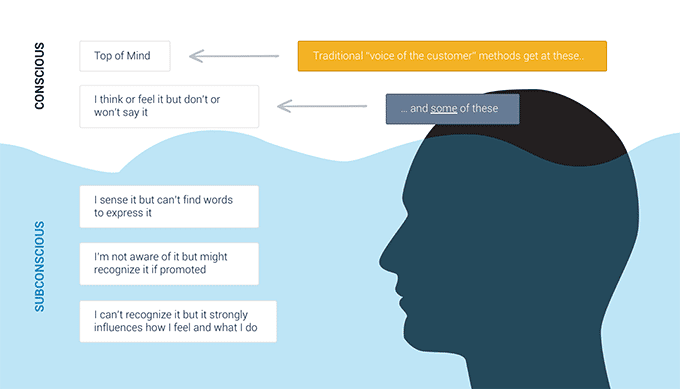
Then although it's important to assume the majority of qualitative enquiry participants aren't maliciously telling untruths, it happens oft plenty to make you lot really think near why it's happening and what y'all can do almost it.
It's also very possible that they simply don't remember an answer. If you are asking a question most whether or not someone will buy from you again in the future (or subscribe to your service), you are likely to get a positive response that doesn't mirror the true future.
These all point to one overwhelmingly articulate blueprint: a clearly poorly designed qualitative research method. Some questions shouldn't be asked in that specific format, or the way the question is asked nigh forces a specific kind of response, leading to a greater alter of untruths. Growing upwardly in the 1990's and early 2000s, I had to fill plenty of forms and always got asked the question of my ethnicity. I could never figure out where I belonged exactly – in what group. Information technology felt limiting and probable lead me to select what felt right but wasn't actually correct.
So let'south intermission it down – why do participants prevarication and what tin can you practice about it?
- Participants care most appearances: When y'all ask for demographical details, income details, employment details, people detest appearing like they're worse off than others.
- Participants want to stay socially viable: If there is something socially unacceptable, people will tend to tell untruths almost the reality of their situation. Think well-nigh a topic like voting – it's socially undesirable to be a citizen that but does non vote or participate.
- Participants are sensitive too: Social and personal questions, including illegal behaviors, may pb participants to tell untruths about realities they bargain with.
- Participants aren't malicious and want to "help:" If they recall that's the respond the research wants to hear, they will requite the answer they believe the research "needs" in order to delight or assist them.
- Participants are human which ways greedy: If there is something in it for them, or they think in that location is, they volition shape the answer to come across their needs.
Ok, this is a little disheartening, but qualitative research is still quite invaluable. The key is how to apply it, using what method, how to conduct information technology and analyze it. Simply get-go…
The basics: what is qualitative research?

Paradigm Source: qualitativeresearch
Elizabeth Wellington describes it well:
"In his book "How Customers Recall: Essential Insights into the Listen of the Market place ," Zaltman characterizes this office of the mind as a "wonderful, if messy, stew of memories, emotions, thoughts, and other cognitive processes we're not aware of or that we tin can't articulate." As customers, we brand decisions from that convoluted (and unexamined) place. Without the amygdalae — the instinctual part of our brain that generates emotions — we wouldn't exist able to make any decisions at all."
Information technology'southward a not a single arroyo, merely rather a very broad systematic collection and organisation and interpretation of textual information.
There is no ane way to conduct qualitative enquiry. It is definitely complicated. The incorrect question can pb to useless data. It definitely requires much organization and categorization. And finally, qualitative data requires deep interpretation and the many methods of doing that. A well-formed question is the key to good research and often leads to more than research and more questions. When you lot consider what a expert research question is, consider that information technology should include the following qualities:
- Information technology is anterior, exploratory
- It'south impartial in the statement, and at that place are no underlying hints given
- Careful focusing on a single idea, don't overdo it by asking besides much
Hither are the ix tips for conducting deep, meaningful qualitative research:

Image Source: qualitativeresearchprocess
one. Prepare a goal
Never brainstorm a qualitative enquiry activity without having oriented yourself with what it is you are trying to larn and attain. Otherwise, you lot volition non be able to codify the right question, nor come up upwardly with the correct machinery and/or setting to conduct your research.
If yous know your goal, and you are familiar with the different methods of conducting qualitative enquiry and the application of those methods; which will be covered afterwards in this blog, y'all will have a better outcome with the research. Ultimately whatever method of research you select based on your goal, will help place what processes must be followed for the best results.
Finally, function of your goals should include who the participants that you are targeting are. Throwing a broad internet to all visitors of a website is less meaningful then selecting a segment depending on the question(due south) beingness asked.
2. Consider the Outcomes
There are few possible products or outcomes that can come out of qualitative research. The outcomes are highly dependent on the type of qualitative research y'all conduct likewise. Some of the outcomes y'all can await include:
- Recurrent themes and hypotheses
- Survey instrument measures
- Taxonomies
- Conceptual models (theories)
"Not everything that tin be counted counts; not everything that counts can be counted."Albert Einstein
One matter to understand almost qualitative inquiry is it's well-nigh never about the numbers, but rather the overall meaning. You're essentially capturing a specific attribute of social or psychological life.
Co-ordinate to Priscilla Esser and Ditte Mortensen:
"When you lot're sharing results from qualitative user research efforts, you're nigh likely focusing on creating an agreement for the lives people atomic number 82, the tasks that they need to fulfill, and the interactions they must result so equally to achieve what they need or want to do."
So, what does that mean for you? Well for one, there are some important considerations to go along in mind, which volition better help y'all interpret the information:
Don't expect a single answer. You will always go a multitude of answers that you must decipher. Looking at the data, don't look at it from a quantitative analysis perspective, because it's not similar that. Yous're a merely telling a story. Your story may not be entirely truthful; however, it MUST exist: plausible, coherent, and if you desire some truth behind it and a stronger case: quantitative data to back information technology upwardly.
three. Know the context to amend understand the responses
A key surface area to think about when it comes to qualitative data is that it's relative.

"Truth can exist compelling without being absolute." Call up ultimately that many truths are relative, specially considering qualitative information.
So, you demand to empathize and think nigh context when you deport and clarify the data coming from qualitative research.
Context includes:
Source of traffic – understand the journey that brought them to your site will assistance you empathize why they respond what they answer. A slap-up place to start is by analyzing the sources of traffic that brought these visitors to your site in the first identify. That way you lot can sympathise their journeying that much better.
Bias – At that place's no way effectually it, qualitative data is tainted with bias. While quantitative data enjoys an absolute truth because numbers are numbers, qualitative data is quite the contrary. Trying to gauge human bias in your sample group is important for context.
Subjectivity – we always say as a gilt rule to optimization is that you want to become from subjectivity to objectivity and data-driven changes. Still, information technology's important to recognize that qualitative data is quite subjective during the analysis process. That's why you want to effort and pain some of that qual information with analytics or other qual data to provide objectivity to a detail issue yous uncovered.
iv. Eliminate Researcher Bias

You lot're biased. Everyone is. Equally a researcher, however, this bias tin stand in the fashion of asking the right questions and seeing other perspectives. So, our recommendation is to accept some sort of a questionnaire or checklist before going into the research to ensure that you practice good reflexivity:
- Consider 5 factors how participants volition view y'all (presumptions)? Considering you are the company asking, how will that affect the answers they give?
- Then consider the v factors that impact the way you analyze data (equally a researcher). Consider what assumptions you, every bit the researcher, have about life, people, website or business organisation, and how those factors may shape your reading of the data.
That brings us to two of import terms that everyone who conducts qualitative research should know: Ontology and Epistemology.
Ontology refers to what is nature of the research vs. the reality. Ultimately, the researcher's philosophical assumptions about the nature of reality.
Epistemology refers to what is possible to know and how we can generate meaningful cognition. Then, the researcher's assumptions on the best ways to inquire to find out the truth. Existence aware of these two terms helps you understand that you also have a bias. Knowing it and understanding what volition assist combat it tin can requite let for a better adventure to ensure your research will not be polluted.
Knowing these two terms will assist you construct "three fundamental questions to your research:
The ontological question: What is the form and nature of reality?
The epistemological question: What is the bones belief nearly knowledge (what tin be known)?
The methodological question: How can the enquiry go about finding what she believes can be known?" (Guba, Lincoln 1994)
five. Beware of subjectivity

Ultimately, researchers oft autumn into the mistake of subjecting histories, assumptions, and values into inquiry the enquiry they conduct. This is why as researchers we must be consciously practicing reflexivity.
Reflexivity refers to the reflective process in which a researcher considers how the findings were produced, taking into consideration the prior knowledge, and our role in it.
half-dozen. Sympathise the Who?
The second most important consideration is the Who of your inquiry. While quantitative research often samples large groups of people randomly, there is a lot more purpose and specificity to the selection of smaller samples for qualitative enquiry. Because the samples are smaller, they must be less random.
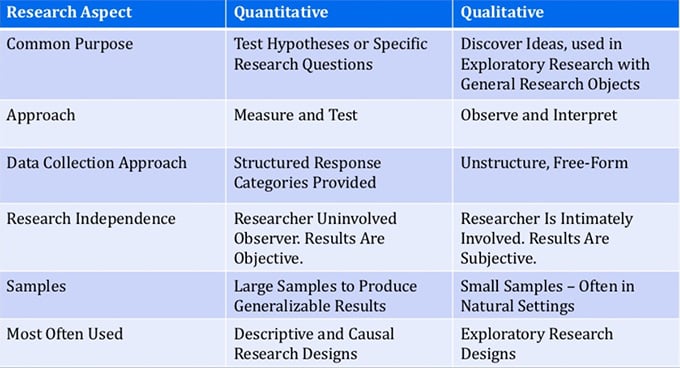
Epitome source: Slideshare
Information Sampling: There are many ways of sampling information, however, for the purpose of this article, we will talk about ii ways:
- Probability sampling: This is selecting a truly random, yet statistically representative sample that can exist generalized to a better understanding of the greater population (market) This is used in quantitative data collection.
- Purposeful sampling: selecting "information-rich cases" (Patton 1990) for deeper inquiry. From these smaller, yet sought-out samples, you tin acquire a cracking deal about bug that are primal to the enquiry. The purpose is to "select data-rich cases whose written report volition illuminate the question nether study." (Patton) This is used in qualitative information drove.
Decide cardinal informants: Again, the aim is at being purposeful when it comes to sampling. Seek out, specific individuals.
Breadth not representatives: You aren't looking for full general public, even so people with the farthermost circumstance that make them eligible for the report. For instance, I'g looking to understand what makes individuals loyal to my brand. The average loyal client shops 2 – iii times a twelvemonth. I would seek out those customers who shop over viii or 9 times a year.
Sample size
- depends on the complexity of enquiry and type of qual research (cannot be clearly determined in advance)
- determined past "theoretical saturation (a betoken at which no new concepts emerge from information)"
7. Select the right Qualitative Research method

Image Source: methodsuxdesign
Qualitative research involves many unlike formats and methods, each with a specific use and aim. The methods include face-to-face or telephone interviews, focus groups, observation (natural settings), textual (polls, surveys).
According to Ditte Mortensen:
"Qualitative methods such as interviews, ethnographic field studies, and (to some degree) usability tests are frequently more than exploratory and seek to get a more than in-depth understanding of the individual users' or user grouping's experiences, motivations, and everyday lives."
Interviews
Interviews should be considered every bit "conversations with a purpose." There are two means to conducting interviews. Contiguous or via phone. While in today's digital world, people are less likely to behave face-face, the chances of accuracy are ever less likely when you tin can't view the person and their expressions when they reply.
Topics and problems to exist covered are specified in advance, in outline form; the interviewer decides sequence and the outline increases the comprehensiveness of the data and makes data collection somewhat systematic for each respondent. Logical gaps in Important and salient topics may be inadvertently omitted. Interviewer flexibility in sequencing and wording questions tin result in the wording of questions in the course of the interview. data can be anticipated and closed. Interviews remain fairly conversational and situational. substantially different responses from different perspectives, thus reducing the comparability of responses.
Useful for:
- Individual perspectives and experiences
- Sensitive topics
- Situations where there is perceived danger of reprisal
- Topics that cannot exist investigated through surveys
- Gathering in-depth information about a topic
Focus Groups
When we think focus group, a lot of times the motion-picture show of a group of people evaluating some sort of product that is going to exist rolled out pops into listen.
According to the Marketing Inquiry Association,
"A focus group is the meeting of a small group of individuals who are guided through a discussion by a trained moderator (or consultant). The goal of the focus group is to go beyond superficial answers and uncover insights on consumer attitudes and behavior."
The primal behind focus groups is trying to generate narrative data in a focused give-and-take. The nature of this format is near the group dynamics offering a wide range of perspectives and views on a mutual experience. Because many people are participating, information technology helps to actuate forgotten details. It'south also revealing in the way people speak nigh issues.
Useful for:
- Characterizing social and cultural norms
- Sharing and comparison
- Revealing how people talk nearly an outcome
- Exploring sensitive topics
Observation

Observation is defined as the recording of the behavior of the sample. Many usability experts use observation and eye-tracking tools when they conduct a study online to specifically gauge more of the participant's facial and body language. Although participants may say they weren't frustrated by a feature or experience post the observation, their trunk language, and facial expressions tell a unlike story. It is all-time used when applied to visitors in their natural environments. For case, if a company that offers teachers classroom management tool wants to understand more than virtually how and when teachers use their product answering questions nigh the agility of the software, they would send a team to classrooms using the software and find over a number of days how the teacher interacts with information technology.
Useful for:
- Individual perspectives and experiences
- Difficult to judge through interview experiences
- Complimenting usability studies
- Topics that cannot be investigated through surveys
- Gathering in-depth information virtually a topic
Textual (polls and surveys)
The go-to for most marketers because it'due south easiest and least invasive. However, with all of the positives, the responses y'all can be getting nearly certain questions may need to be taken with a big spoonful of table salt. Of course, if yous know how to use polls and surveys, and what type of questions work with this format, it can prove useful. What's also key to polls and surveys is first identifying, of course, the goal, but and so the segment that would best provide y'all with the answers that have the greatest specificity and accuracy.
Useful for:
- Specific segment perspectives and experiences
- Broad topics
- Situations where participants can feel free to criticize
- Demographical data
Keep your online surveys as curt and concise
The vast majority of the customers accept a trend to avert long surveys. People do not have the patience nor the time to click through and answer any questions. At that place'due south a higher likelihood that people volition fill out short and articulate surveys. From my ain experience, if I see a question to rate an experience, for example, where I need to click through in order to get to another screen where the question is listed, I will likely opt out. Let it be piece of cake and visible from the outset to increment response rate.
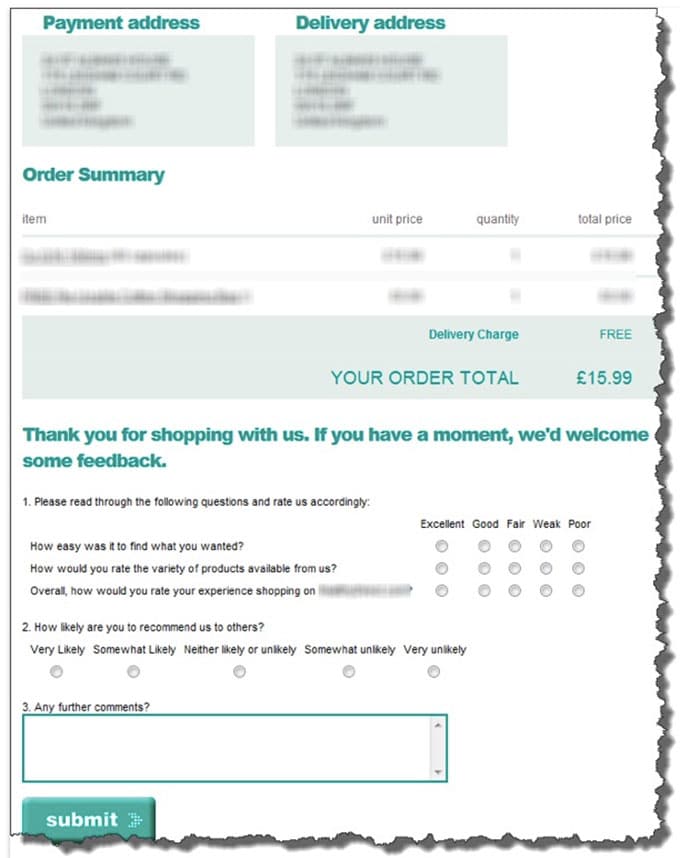
Image source: Econsultancy
Response charge per unit
For qualitative data, the response is more heavily focused on the quality, and non the quantity. For surveys and polls, at that place is a possibility to tap into a greater number of participants. Nevertheless, the aim should not be solely focused on the number of respondents, but rather if you were able to get quality responses from the specific segment you were later.
That being said, with some kinds of polls and surveys (particularly quality or experience assurance or NPS) you need to factor quantity equally well. There are several factors that decide the validity of a survey. Population size, margin of mistake, confidence level, sample size, and response rate.
The Response rate: Number of valid responses / total number of people invited to reply. When you make an investment about annihilation, you expect high ROI (return on investment) of a projection right? The response rate is the ROI of a survey. You need loftier response rate to exist sure that yous are collecting valid data.
Checkout 34 ways to ameliorate your survey response rate:
one. Disguise your survey as a quiz 18. Avoid the spam filter 2. Limit the number of surveys 19. The Anita-effect 3. The ideal survey length 20. Personalize your emails iv. How to observe your demographic 21. Call up of a catchy subject line five. The respondent'due south feel 22. Employ buttons 6. The right type of question 23. The email checklist 7. Respect people's privacy 24. Practise your follow-upwardly 8. How many responses do yous need? 25. Repurpose unopened emails ix. Branded surveys 26. Incentivize 10. Use a progress bar 27. Some people just want to vox their stance eleven. Make the first folio simple 28. Invoke reciprocity 12. Where to ask for demographics 29. No hablo español xiii. Optimize your surveys for all devices xxx. Use images strategically 14. Apply skip logic 31. Offer the opportunity to share the survey fifteen. Use piping 32. Have someone at the other cease xvi. Review the questionnaire 33. Publish your results and act on them 17. Ship out pre-notifications 34. Be grateful By implementing some of the in a higher place strategies, you tin can ameliorate your response rates from 30% to 55%.
PeoplePulse, IBM's innovation center, ran B2B online surveys from 2000 to 2001. After some changes in their survey construction, they managed to double their response rate. The two variables they tested on the surveys were offering incentives and shortening the survey. The incentive increased response rates 10-xv%.
8. Asking the right questions
Depending on the goal and format you will be conducting the qualitative research, your questions volition vary. Whether it'south interviews, focus groups, or surveys, questions need to be identified clearly prior to kickoff the process.
You've considered your goal, idea well-nigh the biases that may pollute your reading of the responses and consider who it is you are request: your job now is to think most the questions.
When it comes to asking research questions, a lot of bias towards the "answer you expect" tin can sway your arroyo to constructing audio, unbiased questions.
Here are some tips to consider:
Apply a verb: Recall, your office is to ask them to describe, characterize, understand, consider. That line of questioning will put the ball in their court.
Identify the topic of interest: Be clear about what the actual topic is first, so ask the question, in lodge to give them context.
Non-directional neutral linguistic communication: Remember, many times we inject our personal feelings into a question which will, in turn, create a bias in the responses.
Define the sample and setting: How will you lot conduct your enquiry – what method? The question may differ based on those decisions. A statement of why you are conducting the research is helpful at this point: like the goal is to Thirty.
Every bit precise every bit possible: Most of the work happens in the question construction phase, if you rush and create a haphazard question, you are likely to go haphazard answers that add no value to your research.
Samples:
To explore the views of men who read 30 skin enquiry blog
To understand XXX company views on XXX
To describe and allocate the factors that determine motivations of visitors for thirty
To understand the knowledge, attitudes, behavior, preferences, and barriers regarding Xxx amongst Xx visitors
To characterize barriers to XXX among male/female person visitors, who are currently enrolled, registered, new, returning, oligarchs,
Mass communication theory has some practiced ideas on how to structure the questions you lot will be asking.
They recommend formatting it into what I would describe as almost a data tree structure.
- The Inquiry Problem
- Goal: or qualitative purpose argument
- Make up one's mind method of research that is best suited to attain the goals
- The inquiry questions (that narrow the purpose):
- Fundamental
- Sub-questions
To hone in on the right questions, Mass Advice Theory suggests using the following scripts to identify the relation between the question and the qualitative purpose statement:
"Central question script (use only one):
"What does it mean to _________________ (central phenomenon)?"
"How would ______________ (participants) draw (central miracle)?"
Sub-question script: "What _________ (aspect) does __________ (participant) engage in equally a _____________ (central miracle)?"
Other tips for asking questions
Have a look at a chart NN Group mentions how to ask open-ended questions:
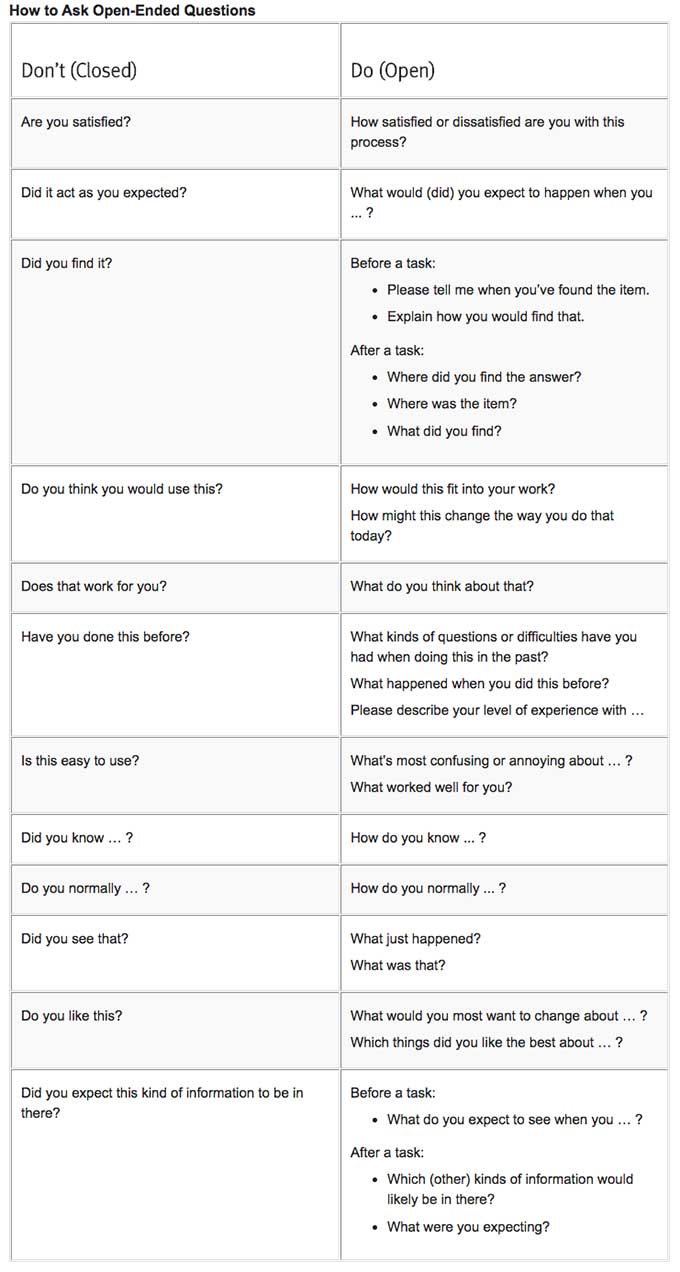
Here are the possible questions to exist asked upon buying procedure:
- What matters to you when ownership product/service?
- How long did the buying process take on average? Exercise you think information technology is curt/long?
- What are we doing worse/amend compared to our competitors?
- Which hesitations did you have earlier buying? Are in that location still any, please clarify?
- What fabricated yous purchase from the states?
- What would you recommend us to better ameliorate our product/service for side by side time?
Andra Baragan states:
"When surveying your customers, y'all don't want to merely survey anyone and anybody. The best way to practise it is to survey only recent customers because they won't hold a biased opinion, and their experiences with you are still fresh. If possible, survey them immediately after they buy. The faster you survey mail-purchase customers, the more authentic your results will be."
9. Conduct Qualitative Data analysis

The part of digital marketing that ever baffles me is the amount of data available for analysis but left unused. There is and then much try that goes into the creation of research, but by the fourth dimension it's said and done, marketers feel exhausted and don't pay close attention to what the results are really maxim.
The key to conducting qualitative data analysis is to ensure there is sufficient, quality data. Looking at that information, at that place are several ways to analyze it. You will have probable considered the analysis needed for your specific qualitative inquiry method previous to receiving the results.
Thematic analysis : identifying themes and patterns of pregnant across a dataset in relation to a research question
Grounded theory: Questions near social and/or psychological processes; focus on building theory from data.
Interpretative phenomenological assay: Assay aimed at seeking insights into the meanings that events and experiences hold for people.
Discourse assay: Analysis of agreement more than nearly how certain terms are existence used. What is said and why information technology might be said?
Narrative analysis: Analysis based on seeking greater understanding of unique perspectives brought on by individuals. Information technology is based on seeing how individuals make meaning using stories. How these individuals make sense of their external and internal globe
Conclusion
Whoever said qualitative data was easy or required niggling precision or attention to detail are the same people that sold AB testing every bit an like shooting fish in a barrel-to-use tool that whatsoever marketer tin merely use to their activities. It is very precise, very scientific, and very driven by knowing who you are targeting, being witting of your biases, and constructing sound problem statements, goals, and questions.

Ayat Shukairy
My name is Ayat Shukairy, and I'm a co-founder and CCO at Invesp. Here's a little more than near me: At the very starting time of my career, I worked on endless loftier-contour e-commerce projects, helping diverse organizations optimize website copy. I realized, that although the copy was great and was generating more foot traffic, many of the sites performed poorly considering of usability and design bug.
View All Posts By Ayat Shukairy
![]()
How Can Researchers Increase The Confidence Business Decision Makers Have In Qualitative Data,
Source: https://www.invespcro.com/blog/9-tips-to-conducting-accurate-qualitative-research/
Posted by: simsbutes1974.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Can Researchers Increase The Confidence Business Decision Makers Have In Qualitative Data"
Post a Comment